🔺 For cellphones 🔺
The BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) is a vital component of your computer that initializes hardware components such as the processor, memory and drives when you start the system. It acts as an interface between your computer’s hardware and software. If you Launch BIOS, you can configure settings like the boot order, and system time, and perform critical system optimizations. If you need to access these settings, here’s a detailed guide on how to run BIOS on Windows 10 and 11.
What is BIOS?
BIOS, or Basic Input/Output System, is firmware embedded in your computer’s motherboard. It plays an essential role during the boot process by initializing hardware, making it possible for the operating system to communicate with hardware components. Accessing the BIOS allows you to change several system settings, such as boot priority, security settings, and overclocking features.
While the steps provided here generally apply to most systems, some variations may exist based on the manufacturer and BIOS version. Some newer systems use UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface), which may have different methods for accessing and using the BIOS.
6 Methods to Enter BIOS Setup on Windows 10 & 11
- Method 1: Access BIOS at Startup
- Method 2: Access BIOS from Windows Settings
- Method 3: Access BIOS via Shift + Restart
- Method 4: Access BIOS Using Setup Key
- Method 5: Access BIOS Through Windows Command Prompt
- Method 6: Using the Run Dialog to Access BIOS
The BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) or UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface) is an essential component of a computer. It helps control the hardware settings and enables the operating system to interact with various hardware components such as the CPU, memory, and storage devices. If you need to adjust certain system settings such as boot order, secure boot settings, or overclocking, entering the BIOS is necessary. Below are the various methods to access BIOS on Windows 10 and 11 systems.
Method 1: Access BIOS at Startup
The most traditional way to access BIOS is during the initial boot BIOS process. When you power on your PC, pressing a specific key immediately after the system starts will allow you to enter the BIOS.
Step 1: Restart your computer and immediately press the BIOS key
Simply start with restarting your computer and as soon as logo appear press the BIOS Key to enter the BIOS. The BIOS key can vary depending on your computer’s manufacturer. Common keys include Del, F2, F10, Esc, and F12. You’ll usually see a message on the screen that says, “Press [key] to enter setup” during boot. Make sure to press the key right after powering on, before Windows begins loading.
List of Common BIOS Keys:
- F2
- Delete (Del)
- Esc
- F10
- F12
- Ctrl+Alt+Del
- Ctrl+Alt+Esc
- Fn + F2 (for some laptops)
BIOS Keys List by Manufacturer
- Acer: F2 or Del
- ASUS: F2 (for most PCs), F2 or Del (for some motherboards)
- Dell: F2 or F12
- HP: F10
- Lenovo: F1 (desktops), F2 or Fn+F2 (laptops), Enter then F1 (ThinkPads)
- MSI: Del
- Microsoft Surface Tablets: Volume Up button
- Samsung: F2
- Toshiba: F2
Step 2: Wait for the BIOS screen to appear
Once you’ve successfully pressed the key, you should see the BIOS or UEFI interface. Here, you can configure settings like boot order, secure boot, or system time.
Additional Tip: If you miss the timing and Windows starts loading, simply restart the system and try again.
Method 2: Access BIOS from Windows Settings
In Windows 10 and 11, you can access the BIOS directly from the Settings menu. This is a particularly useful method if you can’t access BIOS using the traditional key press at startup.
Step 1: Open the Settings menu
- Press Windows + I to open the Settings app.
- Alternatively, you can click on the Start menu and select Settings.
Step 2: Navigate to Update & Security
In the Settings window, go to Update & Security and select Recovery from the left sidebar.
Step 3: Click on Restart Now under Advanced Startup
Under the Advanced Startup section, click on Restart Now. This will restart your PC into a special menu for advanced troubleshooting.
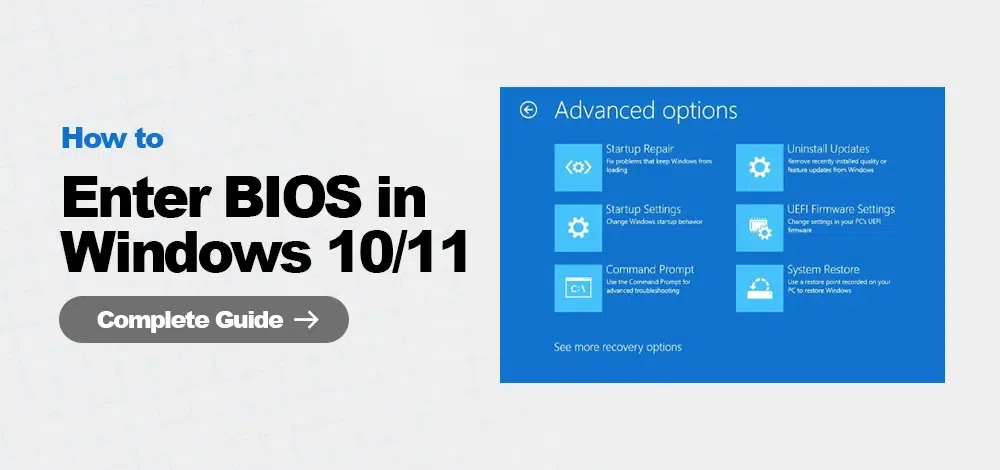
Step 4: Select UEFI Firmware Settings and Restart
Once your computer restarts, you will be presented with a menu. Choose Troubleshoot > Advanced Options > UEFI Firmware Settings, then click on Restart.
Important Tip: This method is helpful if you are unable to press the BIOS key in time during boot-up.
Method 3: Access BIOS via Shift + Restart
You can use the Shift + Restart combination to access the BIOS without needing to navigate through the Settings menu. This method is particularly useful for users who find it difficult to press the BIOS key at the correct time.
Step 1: Click on the Start menu
In the Start menu, click on the Power button.
Step 2: Hold down the Shift key and click Restart
Hold the Shift key on your keyboard and then click Restart from the power options. This will initiate the Advanced Startup menu.
Step 3: Navigate to UEFI Firmware Settings
After your system restarts, select Troubleshoot > Advanced Options > UEFI Firmware Settings and click Restart
Additional Tip: This method works on both Windows 10 and Windows 11, providing a way to access BIOS without using the BIOS key during startup.
Method 4: Access BIOS Using Setup Key
On some computers, especially newer ones, you may be able to access BIOS using a “Setup” key, typically during the initial boot sequence. This method is usually available for systems with UEFI firmware.
Step 1: Power off your computer
Ensure your PC is completely powered off before proceeding.
Step 2: Press the Setup key when turning on the computer
Turn on the computer, and immediately press the Setup key (commonly F2, F12, or Del) when the manufacturer logo appears.
Here’s a list of common BIOS setup keys by manufacturer:
Desktop PCs BIOS Setup Key List
- Acer: F2 or Del
- ASRock: F2 or Del
- ASUS: F2 or Del
- Dell: F2 or F12
- ECS: Del
- Gigabyte: F2 or Del
- HP: F10
- Lenovo: F1
- MSI: Del
- Samsung: F2
Laptops BIOS Setup Key List
- Acer: F2
- ASUS: F2
- Dell: F2
- HP: F10
- Lenovo: F2 or Fn+F2
- MSI: Del
- Samsung: F2
- Toshiba: F2
Other Devices BIOS Setup Key List
- Microsoft Surface Tablets: Volume Up button
- Apple MacBooks: Command + Option + P + R
Step 3: Wait for BIOS Setup to appear
After pressing the key, the BIOS setup screen should appear, allowing you to make changes to your system settings.
Tip: If you do not see the prompt for the Setup key, you can refer to your computer’s manual or the manufacturer’s website for the exact key to press.
Method 5: Access BIOS Through Windows Command Prompt
Another option to access BIOS is by using the Command Prompt to initiate a restart into Advanced Startup. This is an ideal method for users who prefer using commands or need an alternative method when other approaches fail.
Step 1: Open Command Prompt as Administrator
Press Windows + X and select Command Prompt (Admin) or Windows PowerShell (Admin) from the menu.
Step 2: Enter the Command to Restart into Advanced Startup
Type the following command and press Enter:
shutdown /r /o /f /t 00
This command will restart your computer into the Advanced Startup Options screen.
Step 3: Select UEFI Firmware Settings and Restart
From the Advanced Startup Options menu, select Troubleshoot > Advanced Options > UEFI Firmware Settings, and then click on Restart.
Important Tip: This method is especially useful if you’re comfortable with using the Command Prompt and need a quick way to access BIOS.
Method 6: Using the Run Dialog to Access BIOS
This method allows you to access BIOS via the Run dialog box, which is another way to reach the Advanced Startup Options.
Step 1: Press Windows + R to open the Run dialog
In the Run dialog box, type msconfig and hit Enter.
Step 2: Go to the Boot Tab in System Configuration
In the System Configuration window, click on the Boot tab.
Step 3: Enable Safe Boot and Restart
Check the Safe Boot option, click OK, and restart your computer. This will bring up the Advanced Startup Options menu.
Step 4: Navigate to UEFI Firmware Settings
From the restart menu, choose Troubleshoot > Advanced Options > UEFI Firmware Settings and click Restart.
Troubleshooting Tips
- BIOS Key Not Working: If you’re unable to press the correct key at startup, it might be too fast. Try enabling the Fast Boot option in your BIOS or adjusting the Boot Priority in the UEFI firmware settings.
- No BIOS Option Displayed: If you don’t see the BIOS option when pressing the key or using the methods above, it could be that your system uses UEFI. Make sure to access the UEFI Firmware Settings instead.
- Cannot Access BIOS After Multiple Attempts: If you’re unable to enter BIOS after several tries, make sure your keyboard is connected properly, especially if you’re using a wireless or USB keyboard. Wired keyboards are generally more reliable during the boot process.
Conclusion
Accessing the BIOS on Windows 10 and 11 can be done in several ways depending on the manufacturer and your system configuration. Whether you use the traditional key press method or one of the alternative options available within Windows, each method provides a reliable way to access critical system settings. Always proceed with caution when making changes in the BIOS, as improper settings can cause system instability. If you’re unsure about a specific setting, it’s best to consult your system manual or manufacturer’s support page.




Watch the Series.

Watch the Series.
