Upgrading your Windows 10 virtual machine (VM) to Windows 11 can bring a host of new features and improvements to your virtual environment. Whether you’re looking to experience the latest interface enhancements, enjoy more streamlined operations, or utilize updated security measures, moving to Windows 11 within a VM is a strategic way to test the waters before committing to a full update on your primary system.
In this blog post, we’ll walk you through the process of updating your Windows 10 VM to Windows 11, covering all the essential steps and requirements.
What is a Windows VM (Virtual Machine)?
A Windows Virtual Machine (VM) is basically a software-based simulation of a physical computer, running an operating system (OS) within another operating system. In simple terms, it enables you to create an “imaginary” computer on your existing system and lets you run multiple operating systems on a single physical machine at once.
For instance, the Windows 10 VM runs Windows 10 applications without needing separate hardware, but using virtualization software like VMware Workstation, Hyper-V, and VirtualBox, resource allocation (CPU, RAM, and storage) is executed from the host computer.
A VM allows user to:
- Test Software or Applications: Try out new software without affecting your main OS.
- Operating Multiple OS: Run different versions of Windows, Linux, or other operating systems at the same time.
- Simulation of Different Environments: Great for application developers and IT people who want to simulate different network configuration or software configuration.
In case of an upgrade, a Windows 10 VM, a new virtual machine can be readily upgraded to Windows 11 just like a physical machine, provided that all the hardware and system requirements are met. Now that you are clear as to what a Windows 10 VM is, let us see why upgrading to Windows 11 is a good idea.
Comparing Windows 10 VM and Windows 11
Understand these differences before plunging into the upgrade process; they are especially true in the context of virtualized environments. Below is a table that indicates the major differences between the two operating systems, which could help you to appreciate the upgrade to Windows 11 better.
| Feature | Windows 10 VM | Windows 11 VM |
|---|---|---|
| User Interface | Traditional Start Menu and Taskbar | Centered Taskbar, Rounded Corners, New Widgets |
| Performance | Suitable for basic use but limited for advanced tasks | Optimized for performance with better resource management, improved speed |
| Security | Standard security features like BitLocker and Defender | Enhanced security with TPM 2.0, Secure Boot, and improved Windows Defender |
| Virtualization Support | Basic support for VM environments | Enhanced virtualization tools, optimized for virtual environments |
| Direct Storage | Not supported | Supports Direct Storage for faster game and app loading |
| Support for TPM 2.0 | May need to be manually configured | Native TPM 2.0 support required for installation and security |
| Updates | Regular updates with a focus on compatibility | More frequent updates and a more modern approach to system optimization |
| Compatibility | Runs most software applications effectively | Runs the latest apps and games, with better support for new technologies |
| End of Support | Support until October 2025 | Ongoing support with extended updates and improvements |
| Window Management | Multiple desktops available | Enhanced Snap Layouts and Snap Groups for better multitasking |
| Gaming | Decent support for games, but lacks optimizations | Improved gaming experience with Auto HDR and Direct Storage for fast game load times |
As shown in the table above, Windows 11 provides a more modernized user experience, enhanced security, and improved performance, making it a compelling choice for virtualized environments, including Windows VMs.
Why Upgrade Windows 10 VM to Windows 11?
- Improved Security Features: Modern security provisions like TPM 2.0, Secure Boot, and more powerful encryption techniques indicate Windows 11’s appreciation of data safety.
- Performance Enhancement: Windows 11 boasts itself as performance-optimized software, as it offers better resource management in particular, with modern hardware.
- User Interface: Windows 11 rounds off the corners, moves the taskbar to the center, and modernizes systems apps, completing the effect for the better user experience.
- Better Virtualization Support: As a virtual user, you will now benefit from even better virtual support with Windows 11, incl better tools for managing them and a better performance of the system itself in addition to being much more smooth when running workloads virtualized.
- No More Windows 10: The ending of Windows 10 is in October 2025. This acquired upgrading to Windows 11 with all its improvements would ensure continued support via security updates.
Businesses and IT professionals using Virtual Machines will thus have Windows 11 applications upgraded because they will run on the latest applications and satisfy Microsoft’s support policies.
Prerequisite to Update Windows 10 to Windows 11
1. System Requirements: Make sure that your VM meets the minimum system requirements for version 11 of Windows.
- Processor: 1 GHz or higher with at least 2 cores on a 64-bit processor
- Memory: 4 GB or higher
- Storage: 64 GB or more
- Video Card: DirectX 12 compatible or later with WDDM 2.0 driver
- Firmware: UEFI, secure boot capable
- TPM: Trusted Platform Module (TPM) version 2.0
2. Backing Up Your VM: Create a backup of your VM before beginning the upgrade process. In case anything goes wrong, the backup will help undo the changes.
3. Update Check: Make sure the Windows 10 VM has installed patches and the latest updates. That will prevent many issues during the upgrade.
4. VM Software: If you are using any VM software like VMware or Hyper-V, use the latest version that can support Windows 11.
How to Update from Windows 10 VM to Windows 11
Step 1: Check the Compatibility
It’s crucial to check that your Windows 10 virtual machine meets the requirements to use your system in Windows 11. You can use the PC Health Check tool from Microsoft to find out whether your VM is compatible.
- Download the PC Health Check tool.
- Run the tool and verify if your system meets the required specifications.
If your system passes the test, you are ready to proceed. If not, you may need to modify your VM’s settings (e.g., enable TPM or Secure Boot).
Step 2: Enable TPM 2.0 in VM Settings
TPM 2.0 is one of the installation requirements for Windows 11. Here’s how you can enable TPM for your Virtual Machine:
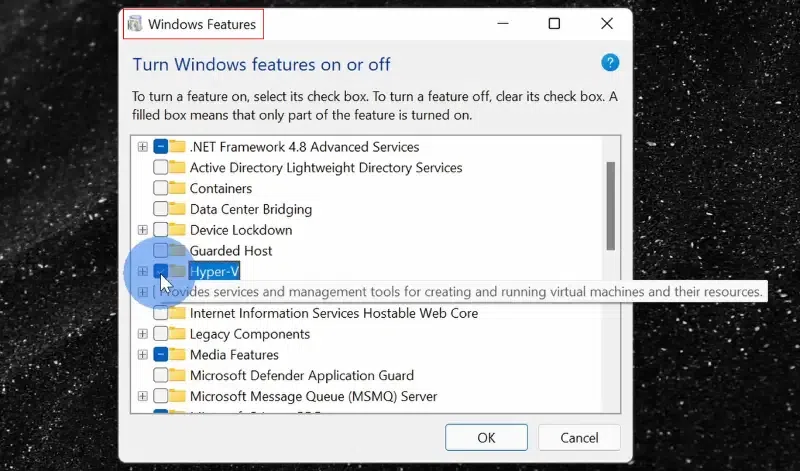
1. Hyper-V:
- In Hyper-V Manager, select your VM.
- Right-click your VM and select Settings.
- In the Security part, tick the Enable Trusted Platform Module box.
2. VMware:
- Launch VMware Workstation and select the VM you will upgrade.
- Under VM Settings, go to the Options tab.
- Select Advanced and enable Encryption. You may have to set up a virtual TPM device.
Step 3: Update the VM to Windows 11
Now, for VM’s initial upgrade, it’s time to meet the upgrade requirements:
Option 1: Upgrade using Windows Update
- Open Settings in your Windows 10 VM.
- Then Update & Security > Windows Update.
- Click on Check for Updates.
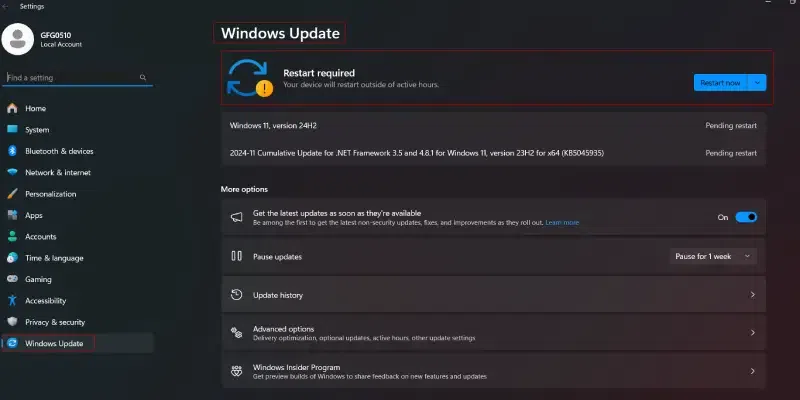
You will see a button that says Download and Install if your VM is eligible for upgrade to Windows 11. Just follow the on-screen prompts to complete upgrade process.
Option 2: Install Using Windows 11 Installation Assistant
- Access the Windows 11 download site.
- Click Download Now under the Installation Assistant section. Follow the prompts that will install Windows 11.
Option 3: Clean Install (for Fresh Start)
For those unable to upgrade, conduct a clean install using a bootable USB or mounting the Windows 11 ISO in your VM software:
- Download the Windows 11 ISO.
- Mount the ISO to your VM’s virtual DVD drive.
- Reboot your VM and follow the installation instructions for a clean install.
Step 4: Post-Upgrade Setup
Once the upgrade is complete, you will need to:
- Check for Updates: Open the app Settings and go to Update & Security > Windows Update. Install any pending updates.
- VM Tools: If you are using either VMware or Hyper-V, reinstall or update the VM tools to ensure dynamic optimal performance.
- Confirm if TPM and Secure Boot are enabled by: TPM 2.0 and Secure Boot should be properly enabled in your VM settings.
Step 5: New Windows 11 in a Virtual Machine
Your Windows 10 virtual machine should now have an upgrade to that of a Windows 11. Take a while to explore the new ones like Snap Layouts, better security options, and totally new taskbar design.
Conclusion
Upgrading a Windows 10 VM desktop to a Windows 11 one can enhance tremendously the performance, security, and overall user experience of your virtual machine. With the procedures in between doing, you are guaranteed the smooth but effective upgrading process of your VM. From making sure of other system requirements to carrying out the upgrade and even with the after post-upgrade checks, this guide helps you ensure everything is right. Whether for personal users, group, or in a corporate environment, there is nothing like adopting Windows 11 on your VM while ensuring you are always using the last features and keeping in line with the latest in security improvements.
How to Update Windows 10 VM to Windows 11 – FAQs
How do I update Windows 10 to 11 directly?
If you’re upgrading from Windows 10, we recommend you wait until you’re notified through Windows Update that the upgrade is ready for your device. To check if Windows 11 is ready for your device, select Start > Settings > Update & Security > Windows Update > Check for updates.
How do you perform VM updates and patches?
To use the Patch feature, you must set up the OS Config API and install the OS Config agent. For detailed instructions, see Set up VM Manager. The OS Config service enables patch management in your environment while the OS Config agent uses the update mechanism for each operating system to apply patches.
Can I install Windows 11 on a virtual machine?
Launch Oracle Virtualbox from your desktop or Start Menu. Click the blue New button. Name your virtual machine; we prefer the name “Windows 11.” You can then choose Microsoft Windows under Type and then choose Windows 11 under Version. Step 4: For this step, you need to allocate resources.
More Tips & Tricks
Linux
- NEW Compress or Extract Files in Terminal
- 25 Basic Linux Commands For Beginners
- How to use 'APT'
- Change Login Background (Mint 22)
- Free Linux Manuals
- Linux Commands from A-Z: free downloadable PDF
- Linux Distros & where to get them
- How to Install Linux Mint
- Dual Booting Windows & Linux
Raspberry Pi
- NEW Raspberry Pi NAS
- Dual Boot the Pi
- NVMe SDD on a Pi
- Clone your Pi SD Card
Free Ebooks
- Crochet
- Knitting
- Loom Knitting
- Cross Stitch
- Windows Manuals
- Linux Manuals
- Raspberry Pi
- Lua
- HTML, CSS & JS
Handy Tools


Learning Linux


Watch the Series.

Watch the Series.
It's FOSS RSS
- This Bachelor's Thesis lets You Build Your Own Kindle Alternative eBook Reader
- New Arch Installer Update Adds U2F Authentication and Bluetooth Support
- wget Removed from Ubuntu Server 25.10 Default Install (And No, It's Not Because of Rust)
- NordVPN Takes on Phone Scammers with Scam Call Protection Feature
- Arch Linux Users at Risk Again as AUR Hit by Another RAT
- Say Goodbye to Microsoft Authenticator! Proton Just Introduced a Solid Alternative
- CISCO Giften AGNTCY Project to Linux Foundation to Standardize AI Agent Communication
- Hands-On with Onlook: The AI-Powered Visual Editor That Blends Code and Design
- Best Linux Laptop of 2025? TUXEDO InfinityBook Pro 15 (Gen10) Launches
- Latest Linux Kernel 6.16 is all Focused on AMD, Intel, and NVIDIA
- How Does OpenMandriva Lx 'Rock' Stack Against Fedora? My Thoughts
- Mastodon Wants Funding and Won't Mind Nudging You for Donation
- Irony? AI-focused Open Source Code Editor Zed Lets You Disable All AI Features
- I Tried Proton's Lumo AI, a Private Alternative to ChatGPT
- Someone Slipped a RAT into Arch Linux!
